Description
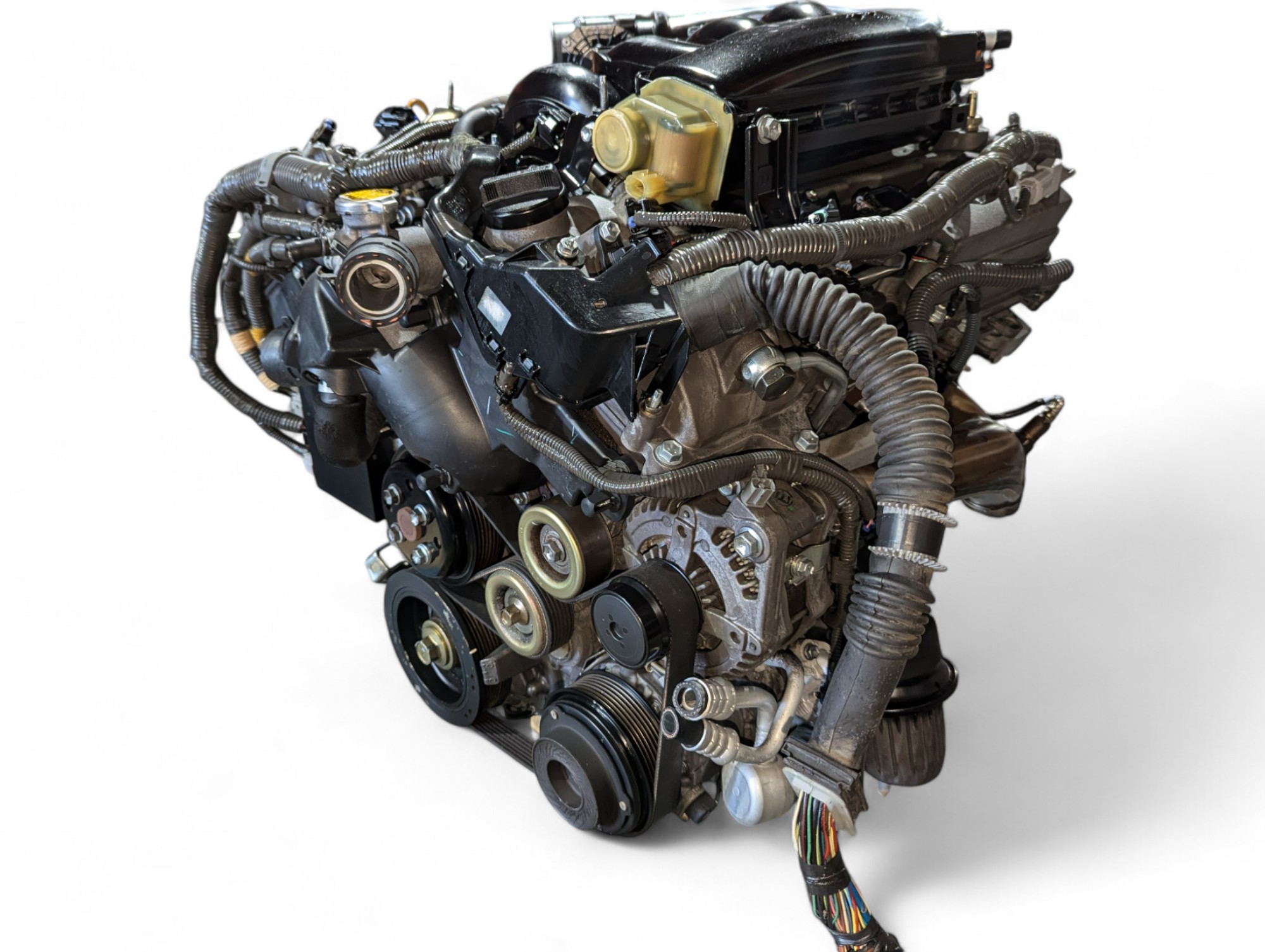
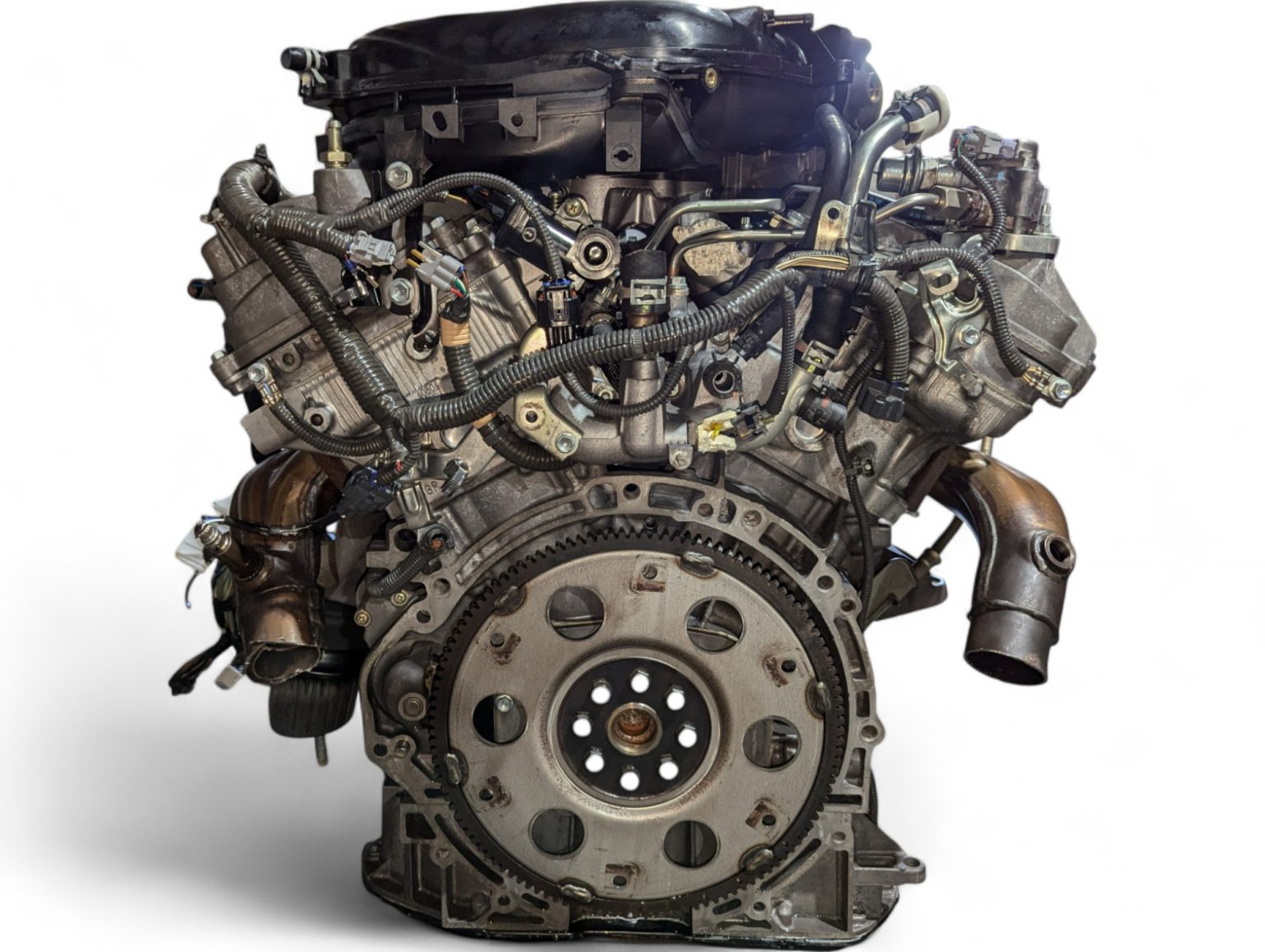
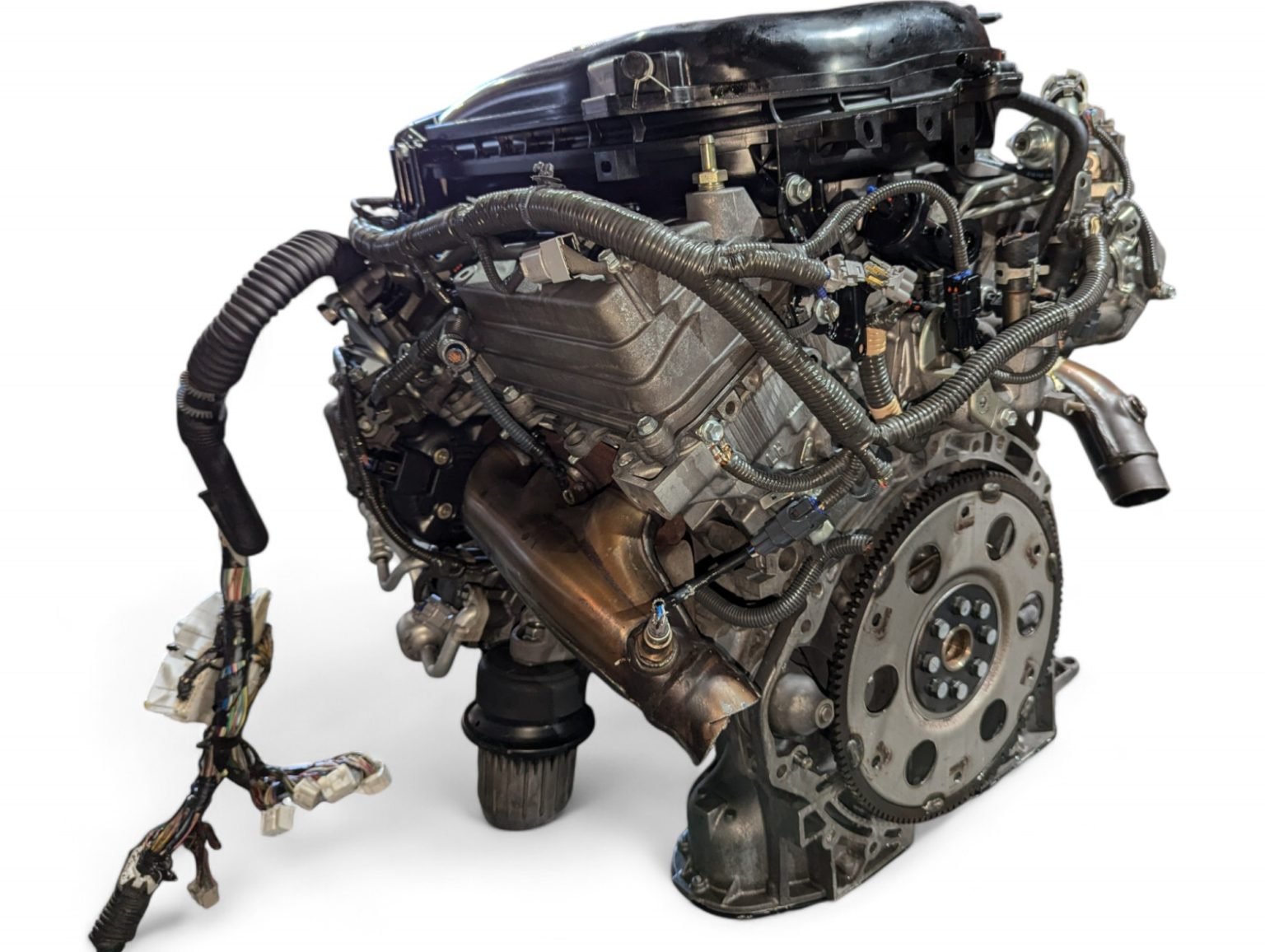
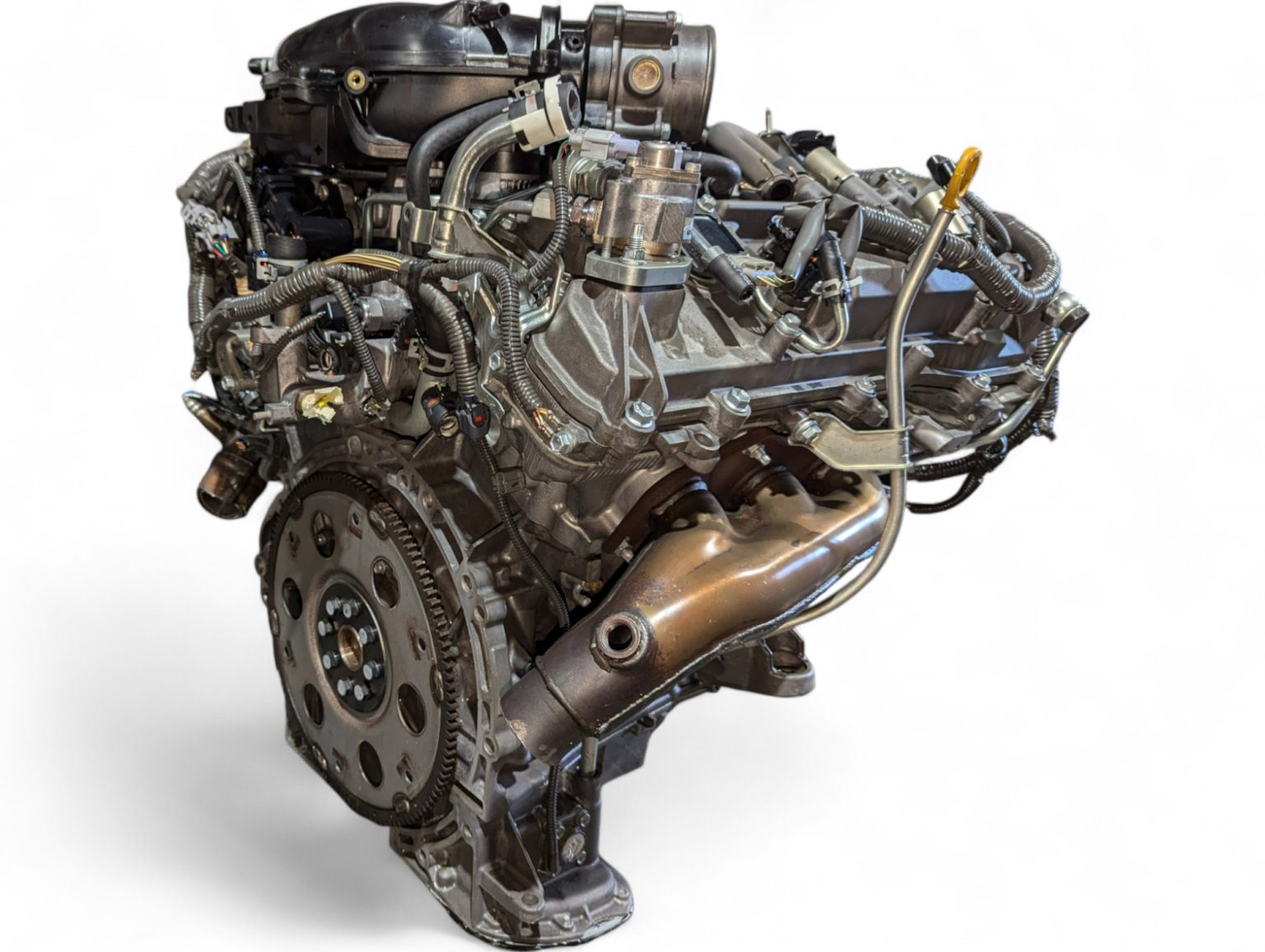
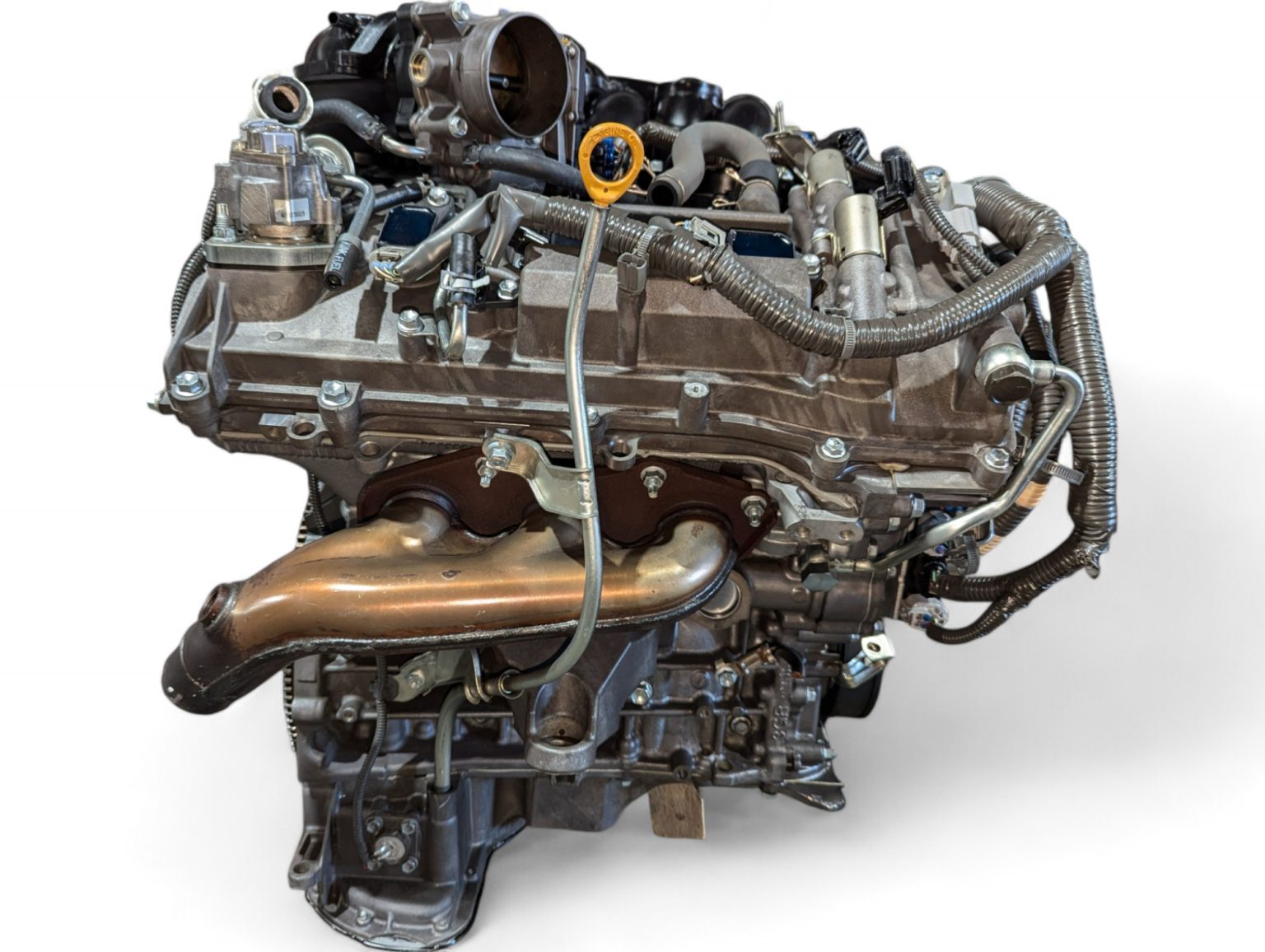
2006 Lexus GS300 3.0L V6 RWD Engine JDM 3GR 0058440 *Damaged* by Lexus is listed under Lexus GS300 Engines. This comprehensive description helps verify fitment, identify part numbers, and plan installation with clarity.
Identification and basics:
– MPN: LEXUS
– Reference price (USD): 1499.00
Key features:
– Correct mounting geometry and verified connectors for the listed applications where specified by supplier data.
– Supplied as shown or stated; ancillaries included only when explicitly specified.
– Traceability: match part numbers and orientation before purchase to reduce returns.
Technical specifications:
– Manufacturer Part Number: LEXUS
Compatibility checklist:
– Confirm drivetrain orientation and bell pattern.
– Cross-check ECU, immobilizer, and sensor compatibility.
– Match emissions family and generation.
– Compare connector shapes, mounting bosses, and hose routing.
Installation guidance:
– Professional installation recommended.
– Replace wear items during install: belts, seals, filters, plugs, fluids.
– Follow torque sequences and prime the oiling system prior to first start.
– Bleed the cooling system and verify fueling integrity.
Post-install checks:
– Perform compression or leak-down tests.
– Scan for DTCs and resolve wiring or vacuum inconsistencies.
– Verify idle quality, fuel trims, coolant temps, and oil pressure at operating temperature.
Packaging and handling: Inspect on delivery and note any damage with the carrier. Keep packaging until functionality is confirmed.
Buyer guidance: Only components explicitly shown or stated are included. If your application differs from the parameters shown, select a variant that matches your configuration.
Search keywords: lexus, gs300, 3.0l, 20-20, jdm, engine, long block, 2006, rwd, 3gr, 0058440.
Fitment notes:
– Measure sensor leads and compare connector indexing.
– Confirm crank and cam trigger patterns match your ECU strategy.
– Verify accessory bracket offsets and pulley alignment to avoid belt walk.
Technical references:
– Use OEM literature for torque specs and lubricant grades.
– Record baseline idle, MAP/MAF values, and coolant temps for diagnostics.
– If swapping, document pinouts and wire colors during harness integration.
Maintenance plan:
– After 100–300 km, re-torque critical fasteners where specified.
– Change oil and filter after break-in. Inspect for metal debris.
– Monitor misfire counters and long-term fuel trims.
Quality checklist:
– Inspect for oil or coolant seepage at gaskets and core plugs.
– Verify PCV routing and vacuum integrity for stable idle.
– Confirm charging output and ground paths under load.
Fitment notes:
– Measure sensor leads and compare connector indexing.
– Confirm crank and cam trigger patterns match your ECU strategy.
– Verify accessory bracket offsets and pulley alignment to avoid belt walk.
Technical references:
– Use OEM literature for torque specs and lubricant grades.
– Record baseline idle, MAP/MAF values, and coolant temps for diagnostics.
– If swapping, document pinouts and wire colors during harness integration.
Maintenance plan:
– After 100–300 km, re-torque critical fasteners where specified.
– Change oil and filter after break-in. Inspect for metal debris.
– Monitor misfire counters and long-term fuel trims.
Quality checklist:
– Inspect for oil or coolant seepage at gaskets and core plugs.
– Verify PCV routing and vacuum integrity for stable idle.
– Confirm charging output and ground paths under load.
Fitment notes:
– Measure sensor leads and compare connector indexing.
– Confirm crank and cam trigger patterns match your ECU strategy.
– Verify accessory bracket offsets and pulley alignment to avoid belt walk.
Technical references:
– Use OEM literature for torque specs and lubricant grades.
– Record baseline idle, MAP/MAF values, and coolant temps for diagnostics.
– If swapping, document pinouts and wire colors during harness integration.
Maintenance plan:
– After 100–300 km, re-torque critical fasteners where specified.
– Change oil and filter after break-in. Inspect for metal debris.
– Monitor misfire counters and long-term fuel trims.
Quality checklist:
– Inspect for oil or coolant seepage at gaskets and core plugs.
– Verify PCV routing and vacuum integrity for stable idle.
– Confirm charging output and ground paths under load.
Fitment notes:
– Measure sensor leads and compare connector indexing.
– Confirm crank and cam trigger patterns match your ECU strategy.
– Verify accessory bracket offsets and pulley alignment to avoid belt walk.
Technical references:
– Use OEM literature for torque specs and lubricant grades.
– Record baseline idle, MAP/MAF values, and coolant temps for diagnostics.
– If swapping, document pinouts and wire colors during harness integration.
Maintenance plan:
– After 100–300 km, re-torque critical fasteners where specified.
– Change oil and filter after break-in. Inspect for metal debris.
– Monitor misfire counters and long-term fuel trims.
Quality checklist:
– Inspect for oil or coolant seepage at gaskets and core plugs.
– Verify PCV routing and vacuum integrity for stable idle.
– Confirm charging output and ground paths under load.